用过Python2.x的小伙伴应该都知道,它默认对中文是不支持的,需要手动设置一下(# coding=utf-8)。这个问题在Python3.x中已经得到了解决,Python3.x中将UTF-8作为了默认编码。但目前仍有大量使用Python2.x的情况,比如我。所以如何正确处理中文是一个十分重要的问题,而这本质上是Python对字符串编码及其转换的问题。
1.不同编码
常见的编码有ACSII、Unicode、UTF-8、GB2312、GBK等。下面简单介绍:
-
ASCII:全称是American Standard Code for Information Interchange,美国信息交换标准代码,最简单的西文编码方案。共有128个字符(数字、大小写字母以及部分特殊符号等),主要用于显示现代英语和其它西欧语言。占1字节。
-
Unicode:统一码、万国码,是计算机科学领域里的一项业界标准,能够使计算机实现跨语言、跨平台的文本转换及处理。
-
UTF-8:8-bit Unicode Transformation Format,是一种针对Unicode的可变长度字符编码。UTF-8用1到4个字节编码Unicode字符。英文占1个字节、欧洲语系占2个、东亚占3个,其它及特殊字符占4个。中文3个字节。用在网页上可以统一页面显示中文简体繁体及其它语言(如英文,日文,韩文)。
-
GB2312:《信息交换用汉字编码字符集》是由中国国家标准总局1980年发布,1981年5月1日开始实施的一套国家标准,标准号是GB2312—1980。基本集共收入汉字6763个和非汉字图形字符682个。占2个字节。
-
GBK:《汉字内码扩展规范》,GBK即“国标”、“扩展”汉语拼音的第一个字母,英文名称:Chinese Internal Code Specification。GBK向下与GB2312编码兼容,是它的升级版,共收录了21003个汉字,支持国际标准ISO/IEC10646-1和国家标准GB13000-1中的全部中日韩汉字,并包含了BIG5编码中的所有汉字。中文占2个字节。
通过上面的介绍可以看到,Unicode是一种通用型编码,其能表示的语言最多,但同时带来的问题是其存储量也较大。而UTF-8可以看作是一种压缩版的Unicode,采用可变长编码降低了数据量。所以一般做法是处理用Unicode,储存用UTF-8,如果只有中文、英文等,则可以用GBK或GB2312进一步减小存储空间。
2.字符串编码判断
在介绍了这些编码方式后,如何判断读取的字符串是什么编码呢?需要用到一个叫做chardet的包,包中有detect()函数,只需传入待判断的字符串即可得到结果。简单使用示例如下:
# coding=utf-8
import chardet
if __name__ == '__main__':
str1 = "你好啊!"
str2 = "Hello"
print chardet.detect(str1)
print chardet.detect(str2)
运行结果如下:
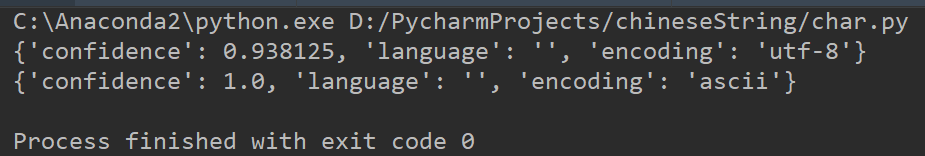
# coding=utf-8
def isUnicode(str):
if type(str) is unicode:
return True
else:
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
# python中unicode编码在字符串前面加u即可
str1 = u"你好啊!"
print isUnicode(str1)
此外可以用以下代码来设置系统默认编码:
# 获取系统默认编码
print 'before default encoding', sys.getdefaultencoding()
# 设置系统默认编码
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8')
# 再次获取系统默认编码
print 'after default encoding', sys.getdefaultencoding()
3.编码转换
在Python中,读取的包含中文的路径、控制台输入的带有中文的字符串等是UTF-8编码,而有时读取的中文内容是GBK或GB2312编码这样就会导致乱码。Python中可以利用decode()和encode()函数进行转码。函数decode()可以实现其它编码到Unicode的转换,函数encode()实现Unicode到其它编码方式的转换。
Python中编码转换的原则是,不管是什么编码都可以直接和Unicode互转,而要想实现如UTF8转GBK,则必须要以Unicode为媒介,先将UTF8转成Unicode编码,再将Unicode编码转成GBK编码。下面以UTF和Unicode互转为例进行介绍。
# coding=utf-8
import chardet
def isUnicode(str):
if type(str) is unicode:
return True
else:
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
# unicode转utf-8
str1 = u"你好啊!"
str2 = str1.encode('utf8')
print chardet.detect(str2)
# utf-8转unicode
str3 = "Hello!大家好"
str4 = unicode(str3, 'utf8')
print isUnicode(str4)
4.编码转换实例
这里以一个实际需求来讲解,遍历获取文件名称(中英文混合),将名称中中文的顿号替换成-,并将结果输出到txt文件中。代码如下。
# coding=utf-8
import os
def isUnicode(str):
if type(str) is unicode:
return True
else:
return False
def findAllFiles(root_dir, filter):
# 将输入字符串同一转成Unicode编码
uni_root_dir = root_dir.decode('gbk')
uni_filter = filter.decode('gbk')
separator = os.path.sep
paths = []
names = []
files = []
for parent, dirname, filenames in os.walk(uni_root_dir):
for filename in filenames:
if filename.endswith(uni_filter):
paths.append((parent + separator))
names.append(filename)
for i in range(paths.__len__()):
files.append(paths[i] + names[i])
paths.sort()
names.sort()
files.sort()
return paths, names, files
def replaceDunHao(string, replace):
if string.__contains__(u'、'):
dun = string.find(u'、')
# 对于unicode字符串,直接+1即可
string = string[:dun] + replace + string[dun + 1:]
return string
def replaceSharp(string, replace):
if string.__contains__(u'#'):
sharp = string.find(u'#')
string = string[:sharp] + replace + string[sharp + 1:]
return string
if __name__ == '__main__':
_, _, files = findAllFiles(".", ".md")
modi_files = []
for item in files:
print item
# 替换中文顿号
while item.__contains__(u'、'):
item = replaceDunHao(item, u'-')
# 替换井号
while item.__contains__(u'#'):
item = replaceSharp(item, u'-')
modi_files.append(item)
f = open("out.txt", 'w')
for item in modi_files:
f.write(item.encode('utf8') + "\n")
f.close()
控制台输出如下:
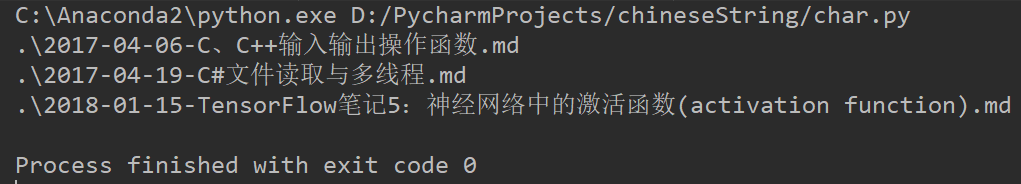

另外插一句题外话,Python中有很方便的方法可以去除List中重复的元素。具体就是先把List转换成Set,然后再将Set转换成List即可。比如下面的代码。
num_list = [1,1,5,3,3,2,7,5]
num_list_new = list(set(num_list))
num_list_new.sort()
上面的代码就是对List中的重复元素进行了删除,同时按照默认从小到大的顺序排序。注意Sort()函数直接对自身操作,是没有返回值的。
5.参考资料
- [1]https://www.cnblogs.com/yunguoxiaoqiao/p/7588725.html
- [2]https://www.cnblogs.com/schut/p/8407258.html
- [3]https://www.cnblogs.com/zihe/p/6993891.html
本文作者原创,未经许可不得转载,谢谢配合

